Submit feedback
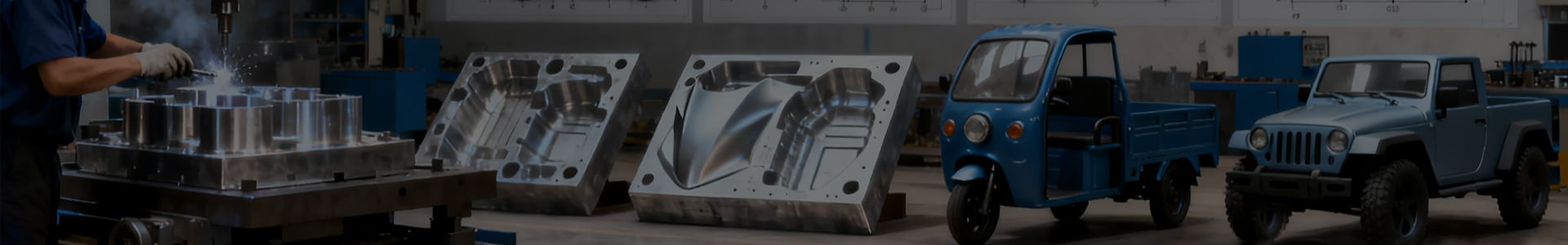
Commercial Vehicle High-Brightness Headlights: What Makes Them Worth Considering?
1. Looking Beyond Drawings: Real Application Context
Technical drawings are essential, but they seldom tell the full story. Commercial vehicles operate for long hours, often under uneven road conditions, exposure to dust, moisture, and repeated vibration. Components mounted on these vehicles are expected to remain dimensionally stable and functionally reliable over extended use.
For lighting systems, this means that Commercial Vehicle High-Brightness Headlights must maintain consistent illumination while fitting within fixed vehicle structures. The housing, internal supports, and mounting features must tolerate thermal expansion and mechanical stress without shifting or loosening.
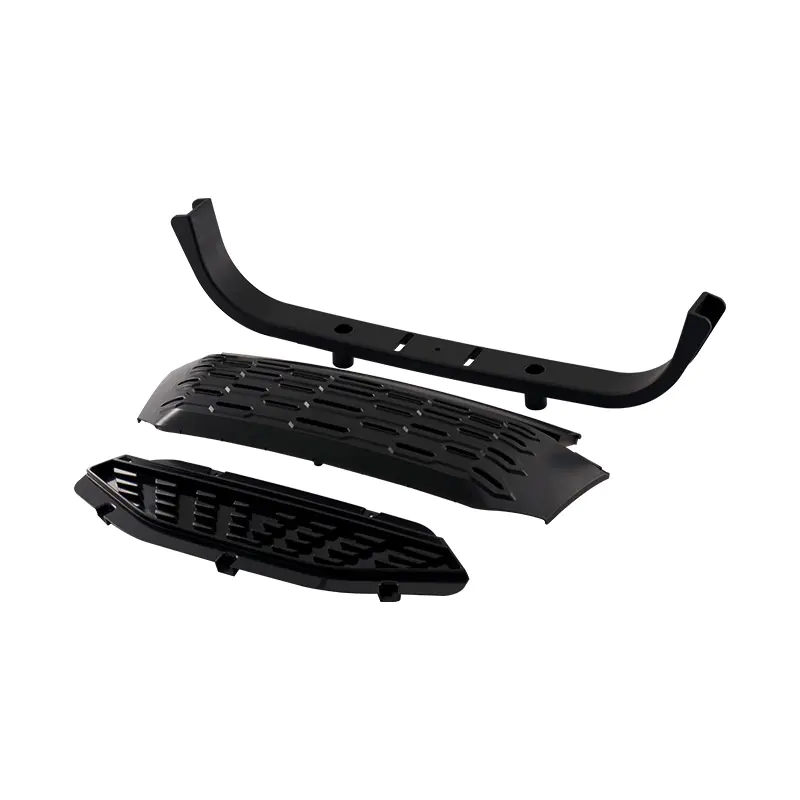

The same logic applies to structural plastic parts. Components produced from an Automotive Support Component Mold often serve as connectors, brackets, or alignment elements. Their performance is tied directly to how accurately they hold other parts in place. In electronics-related assemblies, an Integrated Circuit Mold supports parts that may later be encapsulated, soldered, or mounted on boards, making dimensional stability critical.
2. Early Coordination Sets the Direction
Many production delays can be traced back to early-stage assumptions. When buyers and suppliers exchange only drawings without discussing usage scenarios, revisions often appear later, when changes are more expensive.
Early coordination typically includes:
- Expected annual volumes and project lifespan
- Installation method and surrounding components
- Handling, storage, and transport conditions
Sharing vehicle platform data allows headlight designers to consider wiring routes and fastening methods earlier. In tooling projects, knowing whether a mold will run for tens of thousands or millions of cycles influences steel choice, cooling strategy, and maintenance planning.
For precision tools like an Integrated Circuit Mold, early discussion around downstream processes, such as testing or encapsulation, helps define acceptable tolerance ranges and surface requirements. These conversations shape more realistic designs and smoother project flow.
3. Design Decisions That Affect Manufacturing Stability
Design quality directly influences how smoothly a product moves from prototype to mass production. In lighting components, structural reinforcement around lenses and housings supports a consistent fit and reduces deformation during molding and use.
In an Automotive Support Component Mold, design elements such as wall thickness balance, rib placement, and gate location affect flow behavior and cooling uniformity. Uneven cooling can introduce internal stress, which may not be visible immediately but can cause issues during assembly.
For electronics-related parts, an Integrated Circuit Mold often deals with small features and tight tolerances. Even minor variations in cavity balance or venting can affect fill quality and repeatability. Designing with manufacturing limits in mind helps maintain consistency over long runs.
Stable design is less about complexity and more about predictability.
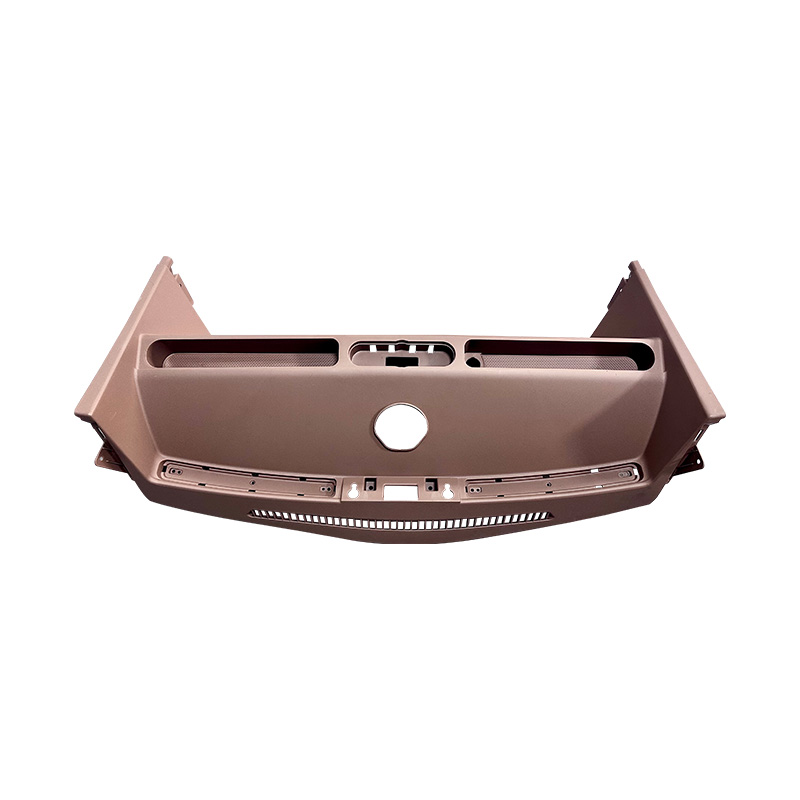

4. Material Choices Influence Long-Term Outcomes
Material selection affects both product performance and tooling behavior. Plastics used in Commercial Vehicle High-Brightness Headlights must handle light exposure, temperature variation, and mechanical load without significant change over time. A material that performs well in short tests may behave differently after extended use.
Tooling materials deserve equal attention. An Automotive Support Component Mold designed for continuous production benefits from steels that balance wear resistance and ease of maintenance. Excessively hard materials can complicate repairs, while softer options may require more frequent intervention.
In precision tooling, an Integrated Circuit Mold often relies on refined steels and controlled surface finishes to maintain detail accuracy. These choices help preserve cavity integrity and reduce variation as cycle counts increase.
| Area | Material Focus | Practical Reason |
| Lighting components | Thermal and dimensional stability | Maintains fit and appearance |
| Structural supports | Strength and fatigue resistance | Supports alignment during use |
| Precision electronics | Surface quality and consistency | Supports downstream processes |
Material decisions made early tend to shape maintenance effort later.
5. Production Efficiency as a Balance, Not a Target
High output is meaningful only when quality remains steady. Factories aim for predictable cycle times, stable filling behavior, and controlled variation rather than chasing shorter cycles alone.
For Commercial Vehicle High-Brightness Headlights, consistency in molding conditions supports uniform surface quality and reliable assembly fit. Sudden adjustments to increase speed may introduce defects that disrupt downstream processes.
Support component tooling often focuses on balanced cooling and smooth ejection to reduce internal stress and surface marks. In electronics tooling, tight control over pressure and temperature supports repeatable detail formation.
Experienced production teams prioritize stability because it simplifies planning, staffing, and quality control over time.
6. Quality Control as a Continuous Activity
Inspection is more effective when it happens throughout the project, not only at final shipment. During early trials, parts are evaluated for appearance, dimensions, and functional fit.
For lighting products, checks may include dimensional measurement, surface inspection, and fit verification with adjacent components. For parts from an Automotive Support Component Mold, cavity-to-cavity consistency is often reviewed to ensure uniform assembly behavior.
In Integrated Circuit Mold projects, inspection can involve magnified surface checks and repeated sampling across runs. Monitoring trends over time helps identify gradual changes caused by wear or process drift.
This ongoing approach allows small adjustments before issues affect larger volumes.
7. Communication Reduces Hidden Costs
Clear communication prevents many avoidable problems. Buyers benefit from explaining not only what they want, but how the part will be used, assembled, and maintained. Suppliers benefit from sharing realistic process capabilities and limitations.
For lighting projects, agreement on testing methods and acceptance criteria avoids disputes later. In tooling projects, clear definitions of allowable variation and change approval processes help manage revisions smoothly.
Transparent communication supports trust and reduces the cost of misunderstandings.
8. Managing Customization Without Over-Complexity
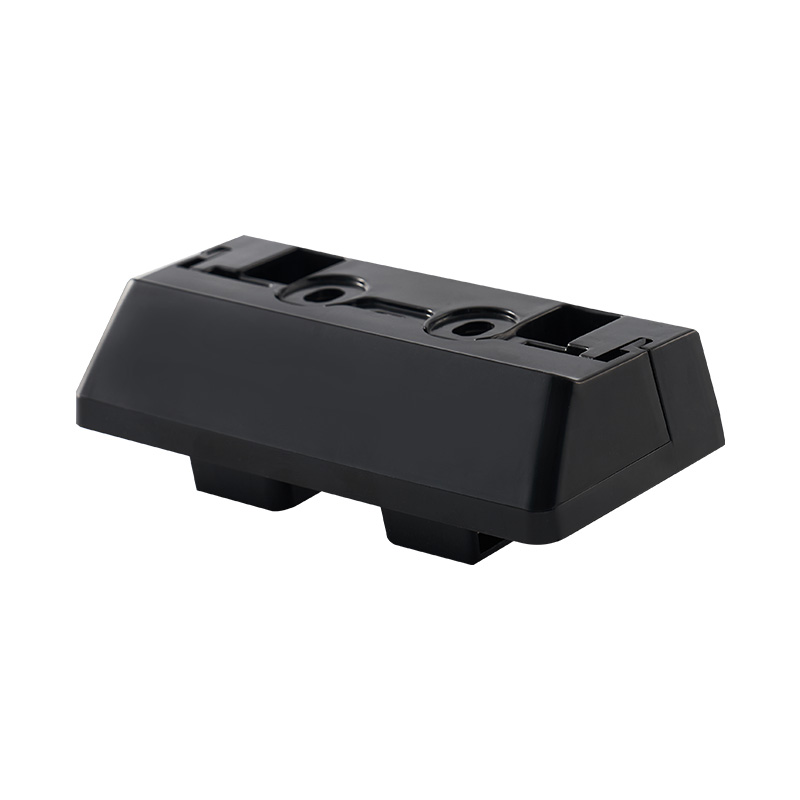

Customization often adds value, but it also introduces risk. Many successful projects strike a balance by combining standardized elements with tailored features.
Standard mold bases, ejector systems, or cooling layouts reduce development time and simplify maintenance. Customized cavities or optical features address specific performance needs without reinventing the entire system.
In lighting assemblies, standardized mounting points paired with customized optics can support multiple vehicle platforms. In structural components, standard reinforcement patterns combined with tailored geometry often meet load requirements efficiently.
This balanced approach supports flexibility while keeping production manageable.
9. Tool Lifecycle and Maintenance Planning
Tooling performance evolves. Wear, thermal cycling, and repeated operation gradually affect precision. Planning for maintenance helps avoid unexpected downtime.
Factories often track:
- Cycle counts and production hours
- Wear-prone inserts or slides
- Historical adjustment frequency
An Automotive Support Component Mold with planned inspection intervals runs more predictably. Precision tools benefit from scheduled checks to maintain dimensional stability.
Maintenance planning supports a steady supply and helps align production schedules with real tool conditions.
Suppliers familiar with Commercial Vehicle High-Brightness Headlights understand lighting-specific constraints. Experience with Automotive Support Component Mold projects suggests awareness of structural and assembly demands. Capability with Integrated Circuit Mold tooling indicates attention to detail and process discipline.
By focusing on real operating conditions, early engineering coordination, appropriate material selection, and clear communication between buyers and manufacturers, projects involving Commercial Vehicle High-Brightness Headlights, Automotive Support Component Mold, and Integrated Circuit Mold can move from concept to mass production with fewer revisions and more predictable results. Emphasizing balanced customization, steady quality control, and planned tooling maintenance helps support consistent output and sustainable cooperation across the entire product lifecycle.