1. What is a Home Appliance Mold?
A home appliance mold is a highly precise tool used in the manufacturing of plastic components for various household appliances, including refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, and more. These molds are critical because they shape molten plastic into exact forms that determine the aesthetic appearance, structural integrity, and functional performance of the final appliance components. In essence, a high-quality mold ensures that every part meets strict dimensional, mechanical, and cosmetic standards while supporting large-scale production efficiency.
By controlling the flow, cooling, and shaping of plastic, home appliance molds enable manufacturers to produce complex components with high repeatability, minimal defects, and consistent quality.
(1)Why Are Home Appliance Molds Important?
Home appliance molds play a pivotal role in product quality and manufacturing efficiency. Their significance includes:
- Surface Finish & Aesthetic Quality – A precision mold ensures smooth surfaces, sharp edges, and consistent appearance, crucial for appliance exteriors and visible components.
- Durability & Structural Stability – Well-designed molds produce components that meet mechanical and thermal standards, enhancing appliance longevity.
- Production Efficiency – Efficient molds reduce material waste, shorten production cycles, and enable high-volume manufacturing.
- Cost-Effectiveness – Minimizing defects and rework reduces overall production costs, making mold quality a key factor in profitability.
(2)Materials Used in Home Appliance Molds
Mold construction involves high-performance materials to withstand repeated cycles and high pressures:
- Steel and Aluminum: Commonly used for the mold base due to their strength, stability, and machinability.
- High-Wear Steel: Used for cavities and core components to resist abrasion, maintain precision, and extend mold life.
- Special Coatings: Anti-corrosion and wear-resistant coatings enhance durability and reduce maintenance frequency.
(3)Typical Applications of Home Appliance Molds
Home appliance molds produce a wide range of components, including:
- Insulation Parts: Such as refrigerator foam inserts and water heater tanks.
- Cushioning Components: Like washing machine anti-vibration pads or air conditioner buffers.
- External Casings & Structural Supports: For refrigerators, washing machines, and other household appliances.
These molds allow manufacturers to maintain consistency and reliability across millions of units, supporting both performance and safety standards.
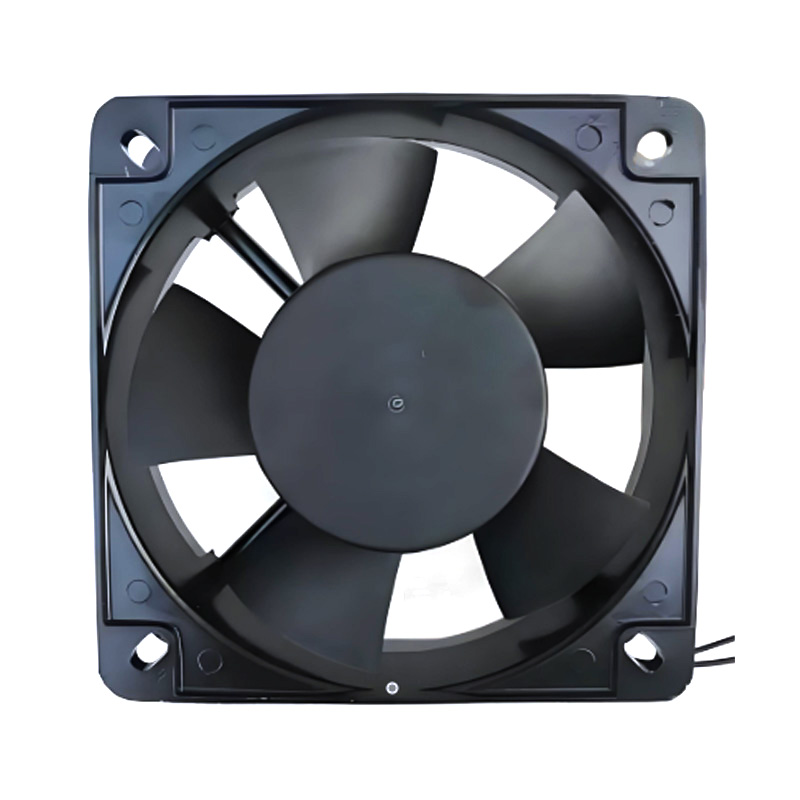
2. What is a Cool Fan Injection Mold?
A cool fan injection mold is a specialized mold designed to manufacture plastic parts for cooling fans. These molds are engineered to ensure high-speed production while maintaining dimensional accuracy and surface quality, which are critical for fan efficiency, noise reduction, and overall performance.
(1)How Does Injection Molding Work for Fans?
The injection molding process for fan components involves:
- Molten Plastic Injection: Plastic material is melted and injected into a precision-engineered mold cavity.
- Cavity Shaping: The mold mirrors the exact shape of the fan blade, hub, and mounting features.
- Cooling and Ejection: The plastic cools, solidifies, and is ejected for assembly into the fan unit.
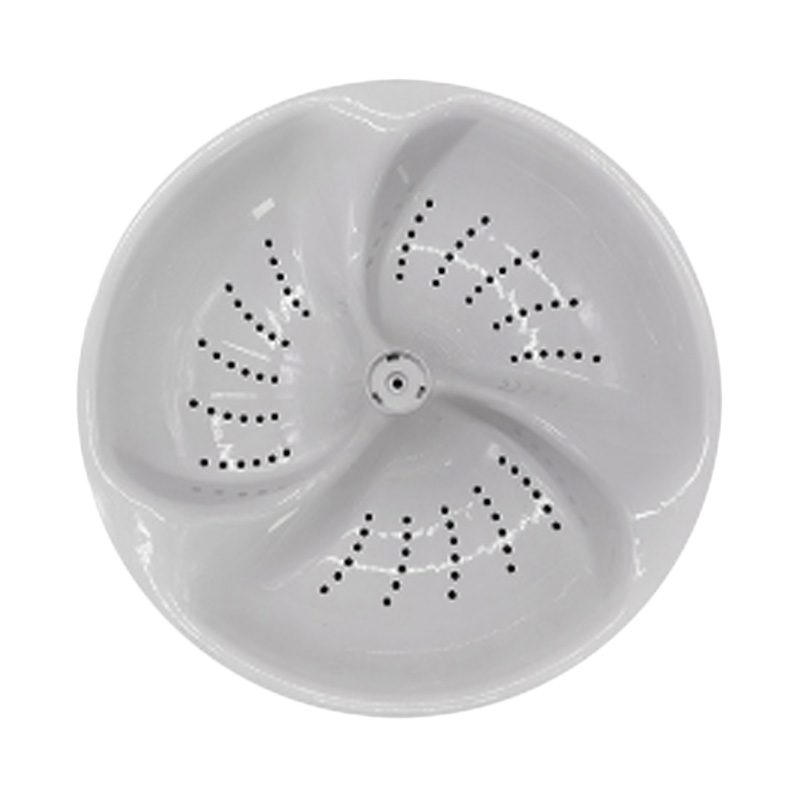
3. What is a Washing Machine Mold?
A washing machine mold is a specialized injection mold used to create critical components such as drum trays, anti-vibration pads, water tanks, and internal supports. These molds ensure that each part meets strict structural, thermal, and dimensional standards, essential for efficient and reliable washing machine performance.
(1)How Does Washing Machine Molding Differ from Other Appliances?
Washing machine molds often deal with larger, thicker parts requiring:
- High impact resistance and strength.
- Anti-vibration design elements to minimize operational noise.
- Cooling channels and surface treatments to speed up production and enhance durability.
(2)Key Features of Washing Machine Molds
- High Cavity Precision: Ensures tight tolerances for critical components.
- Surface Treatments: Provide durability, smooth finish, and resistance to wear.
- Integrated Cooling Channels: Reduce cycle times and improve efficiency.

 +86-18958510469
+86-18958510469



