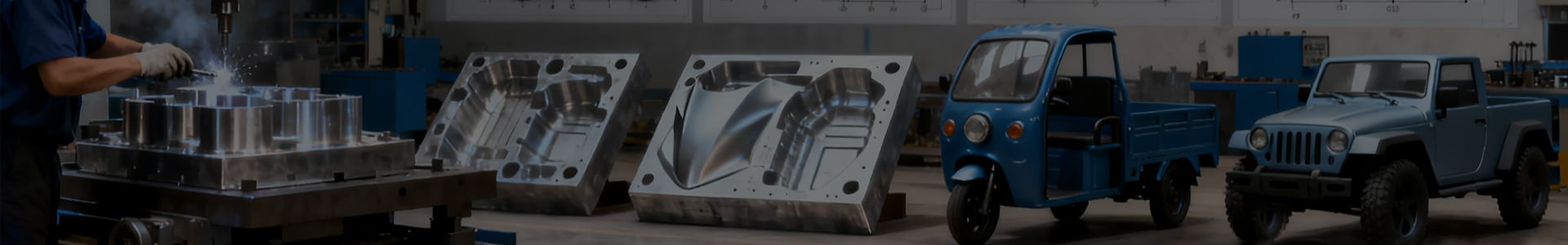
1. What is an industrial supplies mold used for?
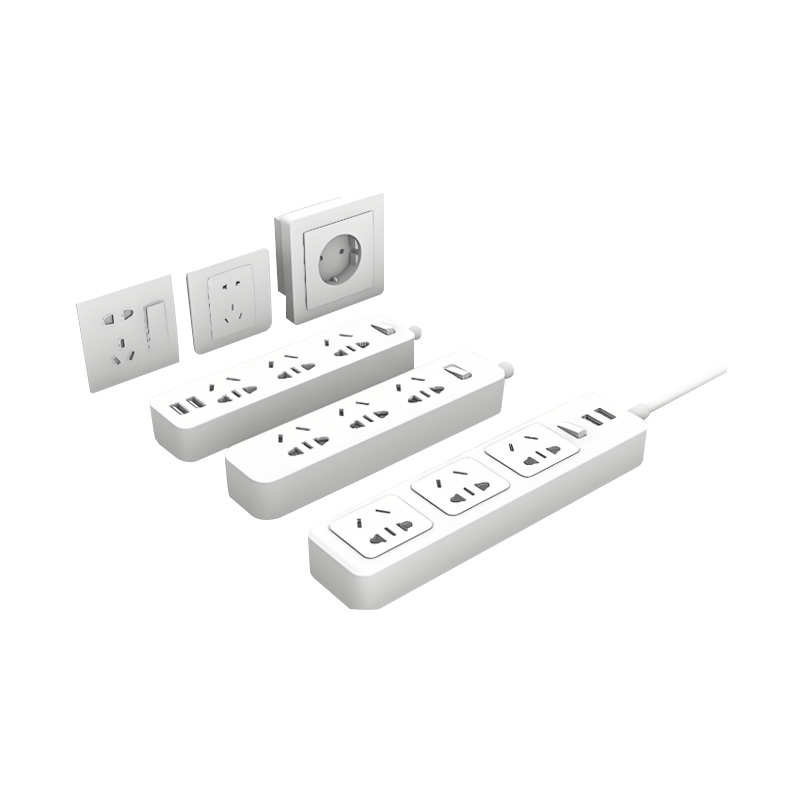
An Industrial Supplies Mold is primarily used to manufacture plastic or metal components that support industrial operations, logistics, storage, and daily production environments. These molds are designed to produce items such as industrial containers, tool housings, equipment covers, trays, bins, and functional structural parts.
Many industrial supply molds are based on injection molding technology, where plastic materials are heated, injected into a precision mold cavity, cooled, and solidified into the final product. This process allows manufacturers to achieve high-dimensional accuracy, stable quality, and consistent output, making it ideal for large-scale production.
Key features and advantages:
- High precision and consistency for mass production
- Ability to form complex structures in one molding cycle
- Reduced assembly steps and lower production costs
- Applicable in automotive, electronics, medical devices, and home appliances
2. How does a plastic storage mold improve mass production?
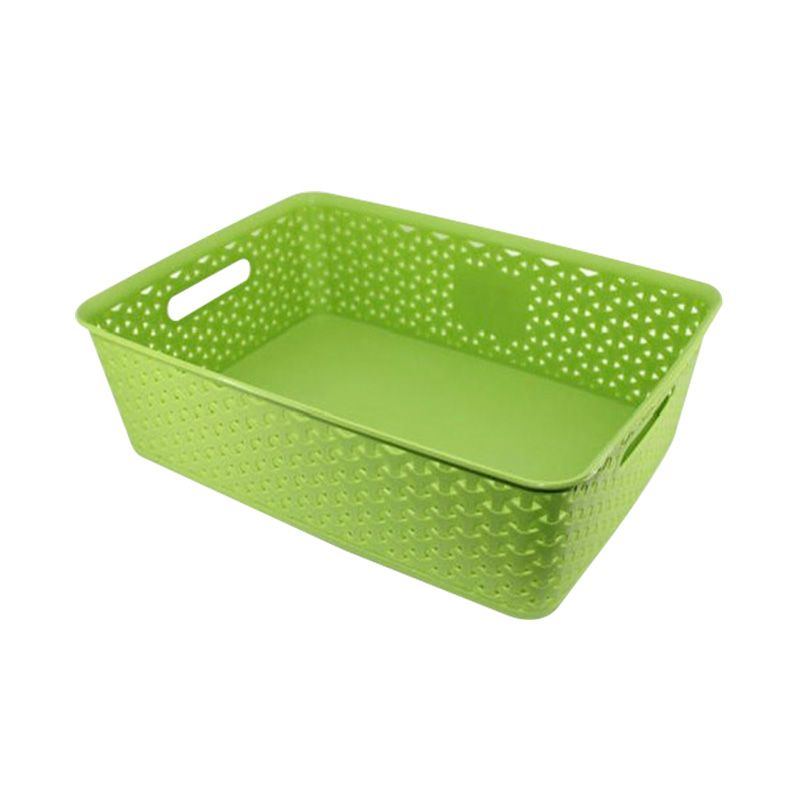
A Plastic Storage Mold is designed to efficiently produce storage-related plastic products such as boxes, containers, bins, crates, and organizational systems used in homes, warehouses, and industrial facilities. Its main advantage lies in enabling high-volume, repeatable, and cost-effective production.
Injection molding is a common process used for plastic storage molds. By injecting molten plastic into a carefully engineered cavity, manufacturers can produce storage products with smooth surfaces, uniform wall thickness, and precise dimensions. This consistency is critical for stackability, load-bearing capacity, and compatibility with automated storage systems.
Plastic storage molds support mass production by reducing cycle time and material waste. Once the mold is installed and optimized, production can run continuously with minimal human intervention. This results in lower unit costs and stable product quality, even at very high output levels.
Advantages for mass production:
- High-volume, repeatable output
- Smooth surfaces and precise dimensions
- Stackability and load-bearing reliability
- Reduced cycle time and material waste
Common molding methods
- Injection molding: Precise filling, uniform walls, suitable for complex designs
- Compression molding: Fast forming speed, smooth surfaces, cost-effective for simpler products
- Plastic storage molds help logistics and storage industries achieve both efficiency and durability, supporting large-scale operations with consistent quality.
3. What are the key components of an injection mold?
The core components include the mold cavity and core, which define the external and internal shape of the product. These parts require high-precision machining to achieve tight tolerances and a well-surface quality. The runner and gate system controls how molten plastic flows into the cavity, directly affecting filling balance and product appearance.
The cooling system is another essential component. By circulating coolant through internal channels, it accelerates cooling and solidification, reducing cycle time and preventing deformation. Efficient cooling improves both productivity and dimensional stability.
Core components:
- Mold cavity and core: Define the shape of the product; require high-precision machining
- Runner and gate system: Controls plastic flow for balanced filling and better appearance
- Cooling system: Circulates coolant to accelerate solidification and prevent deformation
- Ejection system: Includes ejector pins and plates for safe product release
- Guides and mold base: Maintain alignment and structural stability
Industrial supplies molds, plastic storage molds, and injection mold components together form the foundation of efficient industrial manufacturing. By combining precise mold design, great molding processes, and comprehensive mold services, manufacturers can achieve stable quality, high productivity, and long-term cost advantages in mass production environments.

 +86-18958510469
+86-18958510469




